#statusMessage#
Do you want to start the comparison now?
#statusMessage#
Do you want to start the comparison now?
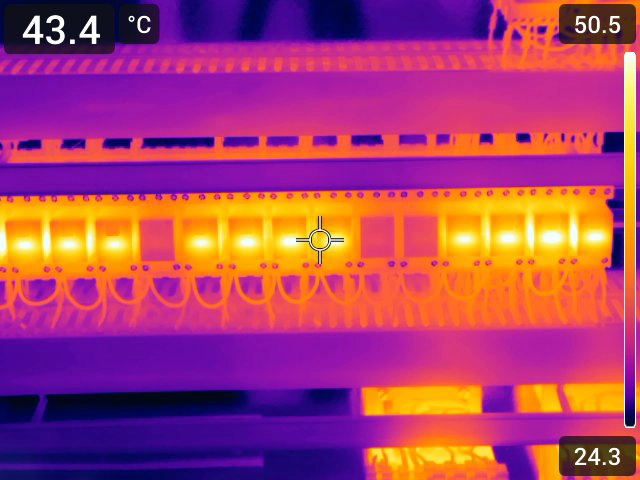

How Thermography Enhances Manufacturing. Machine stoppages, component overheating, or electrical faults—unplanned downti...

Disturbances in the power grid often go unnoticed until systems shut down or equipment fails. Regular power quality asse...

In this practical checklist you will learn how to calibrate your measuring and test instruments effectively – simply, ef...
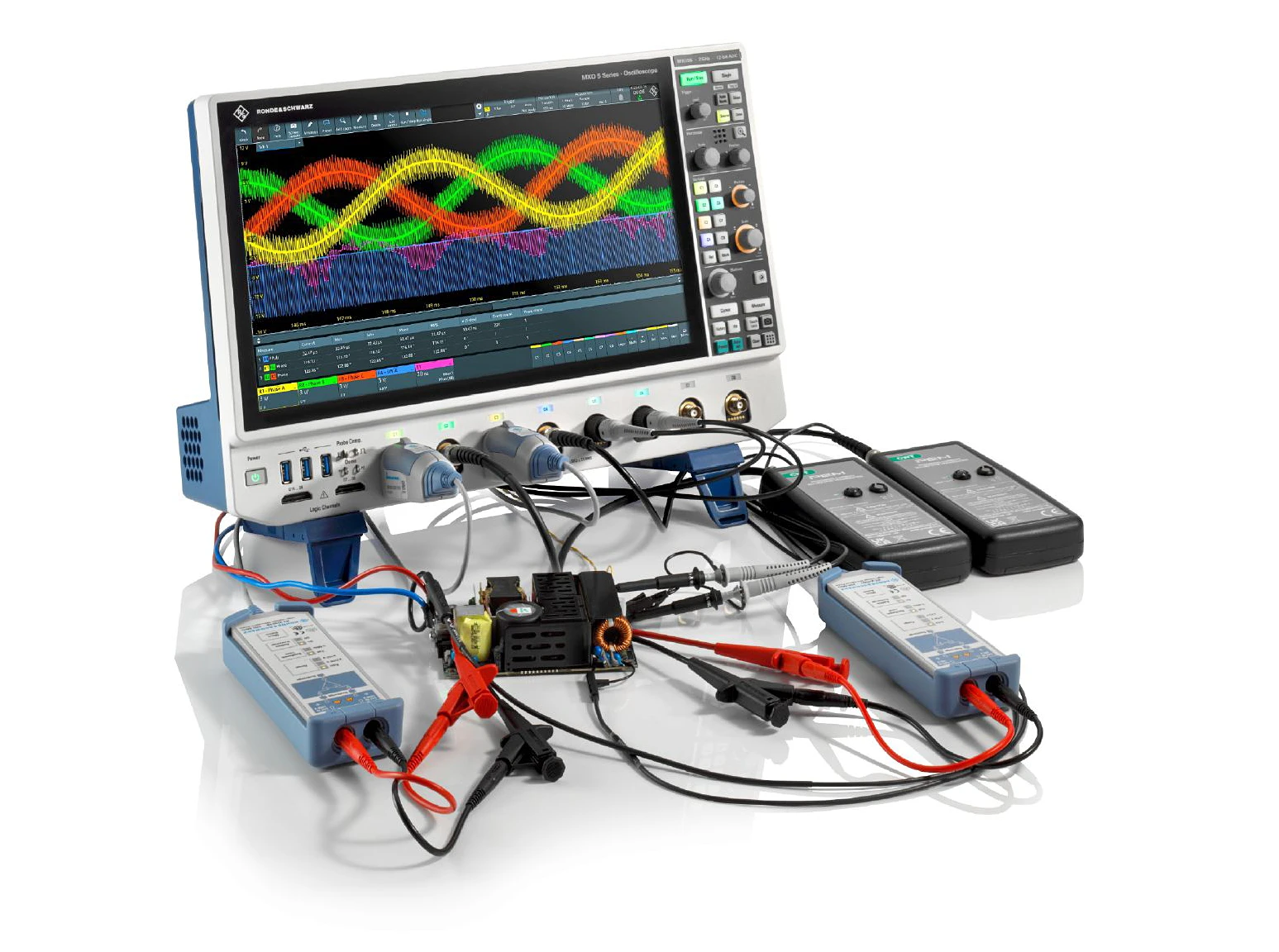
Modern oscilloscopes of the MXO Series from Rohde & Schwarz enable precise analysis and optimization of electric drivetr...
Unfortunately, we no longer have the measuring or testing device you are looking for in our range. But we're sure to have a suitable alternative. Discover a selection of similar measurement products below. Or discuss directly with our experts what your measurement solution could look like.

